![]()
In today’s tech era, automation is the new magic word. Though, we can’t kiss manual testing goodbye. The reason behind it is that manual testing still plays an important role as there are certain scenarios that cannot be totally automated. So, before diving deep into how manual testing is being performed by a tester, let’s first understand what manual testing is.
What is Manual Testing?
Manual testing is the procedure of testing the software with pre-defined test cases without using any automation tools to discover the bug, issues, and imperfection in the software product. The goal of a software tester is to break the system and comprehend the response of the system to various scenarios.
How it is performed?
In manual testing, the observed behaviour of the system is always cross-checked by a tester in opposition to the expected or desired system behaviour. If there is a disparity in both, the tester raises the issue and reports it as a bug. A tester can make use of numerous manual software testing techniques to analyze every feature of the software whether it is functional or non-functional.
- STAGE OF MANUAL TESTING
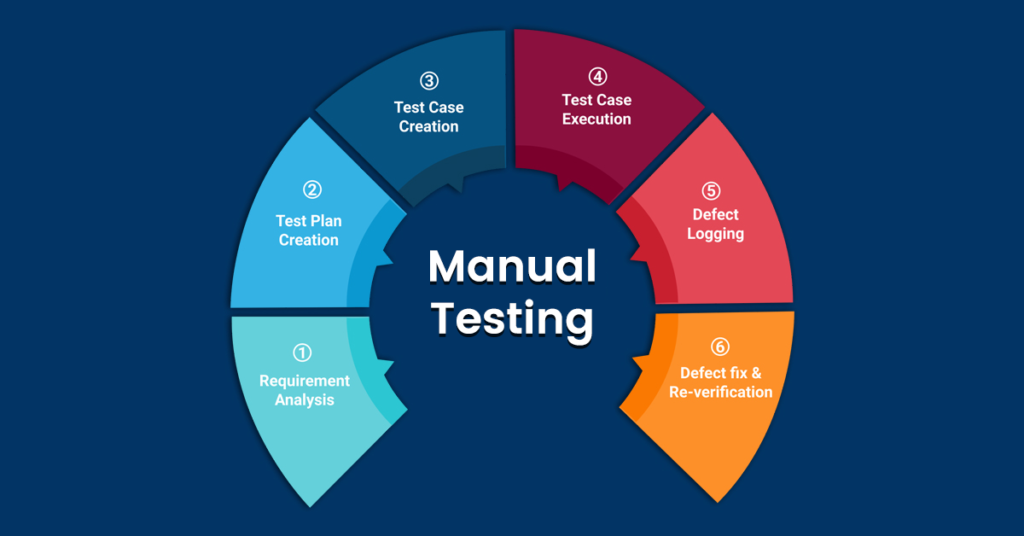
1. Understanding the Client’s Requirement
- A tester first has to be aware of the requirements of the application to be developed and also their functional components.
- By properly understanding it, a tester will be acquainted with the testable component of the requirements. Here the main aim is to ensure the software is bug-free.
2. Prepare Test Plan and Write Test Cases
- Test Planning is one of the imperative activities before preparing the test scenario and test cases.
- Test Plan is the high-level document which describes scope, approach, and other vital information.
- Writing good test cases is significant as it makes the execution of the test cases easy and makes sure high-quality test coverage. A tester can write test cases in the excel file format or any other test management tool.
3. Execution of the Test Cases
- Once all the test cases are written and being approved and environment set up procedure is done; tester can start execution of test cases.
- A tester marks the status of the test cases as Blocked, Not Run, Pass, Fail, Skipped, and many more.
4. Bug Report
- Once all the test cases are appropriately executed, a tester reports the failed test cases as bugs in the defect management tool.
- Manual testing needs heavy investment in human resources. Sometimes, it feels like a mind-numbing job. But, in reality, it is crucial to building websites because automated testing doesn’t cover up the whole thing.
Final Words
In a nutshell, no matter how much-automated testing evolves, manual testing will be an important part of the overall testing routine in the software industry.

